Difference between Single and double cylinder
Difference between Single and double cylinder

Bike cylinder! Single cylinder! Double cylinder! What biker friends' names doesn't sound familiar? But do you know what a bike cylinder actually is? Stay with us and read the article in detail. Today, We Team Motorcycle Valley will discuss bike cylinders. So let's get started without further delay.

All fuel engines have cylinders. Engine processes are completed within the cylinder. And the engine has one or more cylinders to complete these processes. Today we will only talk about motorcycle cylinders.
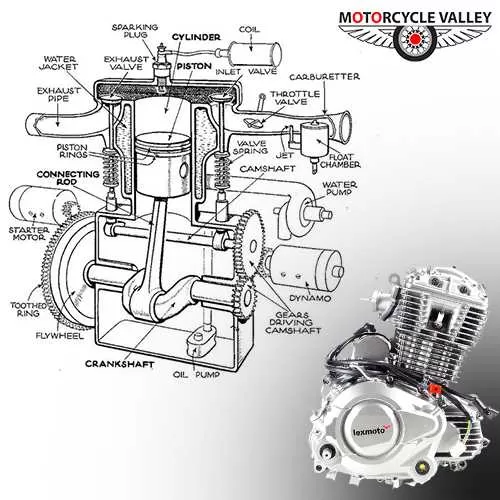
Single cylinder:
1. The engine will have only one cylinder, and the entire process will be done in that cylinder.
2. Bikes ranging from 80 to 500 cc have this single cylinder.
3. Single-cylinder engine manufacturing costs are also low, and this engine is also easy to manufacture.
4. Mileage is pretty good.
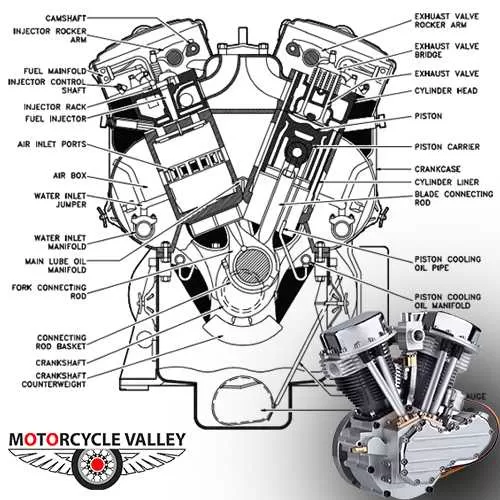
Double cylinder:
1. There are two cylinders in the engine.
2. Engine processes are completed separately in the intake cylinder to produce power.
3. 500+ cc bikes have this double-cylinder engine.
4. Due to the CC, double cylinders are installed instead of single cylinders to reduce the engine vibration of the bikes and get smoother performance.
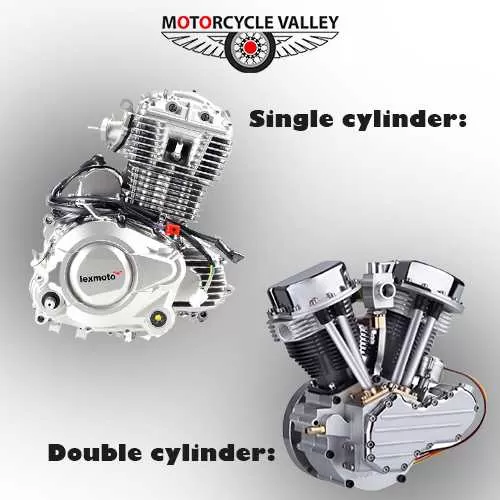
Difference between Single cylinder and double cylinder:
A bigger engine needs more power, so the CC of the bike is higher. The single-cylinder takes some time to generate that power. Because of this, the engine performance is not that good, and the bike vibrates. But if there is a double cylinder in that place, the power of the second cylinder is also generated as the first cylinder provides power. Due to this, there is no vibration in the engine. But it is good to say that the same amount of power is generated from single and double cylinders.
Generally, motorcycles in our country have single cylinder engines. But in other countries, high-cc bikes have double cylinders in their engines. To understand the difference between single and double cylinder engines, you must first understand how the engine works.
Each engine has 4 strokes. Each stroke works differently. The four strokes of the engine are: 1. Suction, 2. Compression, 3. Expansion, and 4. Exhaust. Now let's describe the work of these 4 strokes.
1. Suction Stroke: In this stroke the charge of air and fuel mixture is taken inside the cylinder. To accomplish this process, the piston moves downwards from the cylinder head.
2. Compression Stroke: By completing the process of Suction Stroke, in this stroke the mixture charge of air and fuel is compressed.
3. Expansion Stroke: This stroke is also known as the power stroke. In this stroke, the compressed charge is ignited, which creates superheated gases inside the cylinder. And the piston is pushed down the cylinder head by this gas, causing the hot gases to expand.
4. Exhaust stroke: This is the last step of the complete cycle. Which is known as the heat rejection process. In this stroke, the piston moves from the bottom of the cylinder to the top, forcing the hot gas out of the cylinder. The engine runs on this gas.
Bike engine process is done by these 4 strokes in the cylinder. If there are multiple cylinders, the process is repeated in the opposite cylinder.
Bike News

Among the foreign brands in Bangladesh, the Thai motorcycle brand GPX has earned a great reputation even for ordinary bikers w...
English Bangla
Suzuki is one of Japan's most recognizable motorbike brands renowned for its capable, performance-tuned, and stylish two-wheel...
English Bangla
Yamaha has organized a test ride of Yamaha's only higher cc bike Yamaha FZ25 in Bangladesh, where not only Yamaha bike users but...
English Bangla
Lifan is a very well-known bike brand in the biker community in the motorcycle market of Bangladesh and one of the reasons beh...
English Bangla
Yamaha has launched its high-cc bike, the Yamaha FZ 25, in the Bangladeshi market, creating quite a buzz among motorcycle enth...
English Bangla